In modern America, longevity is on the rise, with individuals now enjoying longer lives. Upon reaching the age of 65, the CDC reports an average additional life expectancy of 19.3 years. Consequently, for many seniors, maintaining good health and managing chronic conditions are essential components of their senior living experience.
Embracing a healthy lifestyle is paramount in mitigating senior health risks and ensuring a higher quality of life during one’s golden years. Dr. Jeanne Wei, the executive director of the Reynolds Institute on Aging at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, underscores the importance of choices such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and adopting a balanced diet. Furthermore, enlisting the expertise of a geriatrician, a medical specialist attuned to the unique health concerns of aging individuals, can provide invaluable guidance in managing chronic conditions and optimizing overall well-being. By incorporating these measures into your senior healthcare regimen, you can join the ranks of the 41 percent of individuals aged 65 and above who report excellent or very good health, according to data from the CDC.
-
Advertisement
1 High blood pressure

High blood pressure is often called a "silent killer" because it doesn't usually cause any noticeable symptoms. But it can harm your heart, kidneys, blood vessels, and brain even without you knowing it.Although it might seem like only a small number, seven percent of women aged 20 to 34 have high blood pressure. The problem is that many young adults with this condition often go undiagnosed and untreated. If you don't address high blood pressure, it can lead to heart problems later in life and is the top reason for strokes. The good news is that by simply managing your blood pressure, you can reduce your risk of having a stroke by 48 percent. So, taking care of your blood pressure is really important, even when you're young.
-
2 Arthritis
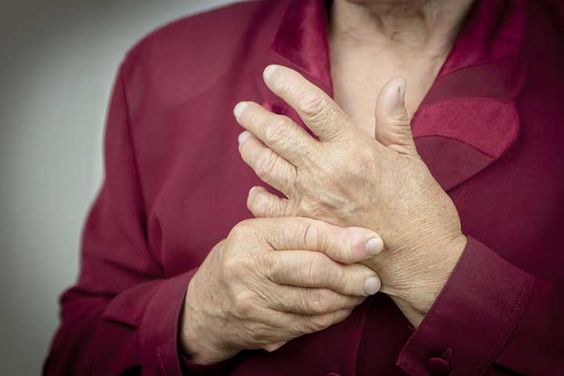
Dr. Marie Bernard, a respected geriatrician and Deputy Director of the National Institute on Aging in Bethesda, Maryland, underscores the significant impact of arthritis among individuals aged 65 and older. The statistics provided by the CDC, revealing that nearly half of all adults in this age group are affected by arthritis, underscore the magnitude of this health challenge. Arthritis can manifest as pain and diminished quality of life for many seniors, potentially discouraging them from engaging in physical activities. Nevertheless, it is crucial to collaborate closely with a healthcare professional to craft a personalized activity plan tailored to individual needs. This personalized approach, when combined with other appropriate treatments, plays a vital role in preserving and promoting the overall health and well-being of seniors, ensuring they can continue to lead fulfilling lives as they age.
-
3 Heart Disease
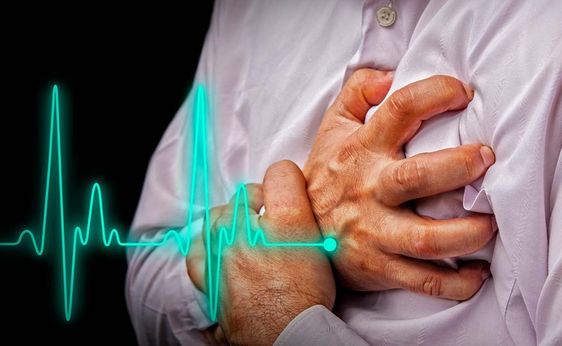
When we think ofheart disease the immediate image that often comes to mind is a heart attack. However, it's important to understand that heart disease is a broad term encompassing various conditions that can negatively impact your heart's functionality. These conditions encompass coronary artery disease, arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Each of these conditions presents unique warning signs and symptoms that should not be ignored. Being aware of these warning signs and knowing how to react is crucial for maintaining heart health and seeking timely medical attention when needed. By understanding the diverse aspects of heart disease and staying informed, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart and overall well-being.
-
Advertisement
4 Colon and rectal cancer

The increase incolon and rectal cancersamong millennials is a concerning trend that has been observed in recent years. While age is indeed a significant risk factor for colorectal cancer, there has been a noticeable rise in cases among younger individuals, and researchers are trying to understand the reasons behind this shift. Several factors could contribute to this phenomenon:
-
5 Fatty liver diseases

Fatty liver diseases, such as nonalcoholicfatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), manifest when an excessive accumulation of fat occurs within the liver. Left untreated, these conditions can progress to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, and in extreme cases, liver failure. Typically, individuals who are overweight or obese are at a higher risk of developing NAFLD and NASH. However, these conditions can also affect those with insulin resistance, elevated levels of fat in their blood, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and specific genetic predispositions. Fortunately, there is hope for those struggling with these conditions, as losing just 3% to 5% of one's body weight, especially if overweight or obese, can play a crucial role in reducing fat accumulation in the liver and potentially mitigating the progression of these diseases.
-
6 Brain shrinkage

Brain shrinkage, often a daunting concept, is actually a natural aspect of the aging process. Nevertheless, specific factors are associated with an accelerated decline in brain volume. Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, or smoking have been linked to a more rapid rate of brain shrinkage, potentially impacting cognitive function, according to Michos.A compelling study underscores the significance of making heart-healthy choices during one's 20s, as it can serve as a safeguard against future brain shrinkage. Moreover, this research strengthens the argument for maintaining overall health to preserve cognitive abilities. It reveals a concerning correlation, indicating that individuals with risk factors for heart disease tend to accumulate more amyloid deposits in the brain, which are closely associated with Alzheimer's disease.
-
Advertisement
7 Obesity

Obesityis strongly associated with a multitude of health problems, particularly chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, depression, stroke, and cancer. Additionally, it can pose significant risks during pregnancy, leading to gestational diabetes, and is linked to higher rates of infant mortality.The economic impact of obesity is substantial, with the CDC estimating annual medical costs exceeding $170 billion. Measures aimed at addressing obesity, such as banning sugary soft drinks from kids' menus, have stirred controversy. Furthermore, obesity intersects with the issue of food insecurity, highlighting the complex relationship between nutrition and health. Public health initiatives often prioritize tackling food hunger, particularly among children, in an effort to combat the multifaceted challenges posed by obesity and its associated health and socioeconomic consequences.
-
8 Depression

In 2019, around 280 million people had depression, including 23 million kids and teens. Depression is more than just feeling sad sometimes; it's when you feel really down or lose interest in things for at least two weeks. During a depressive episode, you might feel sad, irritable, or empty most of the day. You could also have trouble concentrating, feel guilty or worthless, think about death or suicide, and have sleep or appetite changes, or low energy. Depression increases the risk of suicide, but there are helpful treatments. Talking to a therapist can work, and sometimes, depending on your age and how severe it is, medicine can help too.
-
9 Gout

Gout, a form of arthritis, is characterized by its distinctive symptoms of painful joint inflammation and swelling. The root cause of gout lies in the accumulation of uric acid crystals within the joints. Several factors contribute to the risk of developing this condition. Obesity is a notable risk factor, as excess body weight can lead to an increase in uric acid levels. Additionally, being male is associated with a higher susceptibility to gout. High blood pressure, another risk factor, can further elevate the likelihood of experiencing gout attacks. Dietary choices play a significant role as well, with foods rich in purines being culprits in gout development. These purine-rich foods, which include red meat, liver, and anchovies, can exacerbate uric acid buildup. Understanding and managing these risk factors, along with adopting a diet that minimizes purine intake, are essential steps in preventing and managing gout, a condition that can cause considerable discomfort and joint damage if left unchecked.
-
Advertisement
10 Diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas

Being overweight or obese can significantly increase the likelihood of developing gallbladder diseases, including conditions like gallstones and cholecystitis. Individuals with obesity often exhibit elevated levels of cholesterol in their bile, a key factor contributing to the formation of gallstones. Moreover, obesity can lead to an enlarged gallbladder that functions less effectively.Interestingly, carrying excess weight around the waist area can also raise the risk of gallstone development. Paradoxically, rapid weight loss can further heighten this risk. For those grappling with obesity, it's crucial to engage in a conversation with a healthcare professional to explore safe weight loss strategies.
-
11 Bipolar Disorder

In 2019, a lot of people, around 40 million, had bipolar disorder (1). Bipolar disorder makes people feel very sad and sometimes very happy or irritable. It's like a see-saw of emotions. When they are sad, it feels like a heavy cloud over them, and they may not enjoy things they used to. When they are super happy, they have lots of energy and might talk a lot, have racing thoughts, or do risky things.
People with bipolar disorder can sometimes feel so bad that they think about hurting themselves. But there are ways to help them feel better. They can learn about their condition (psychoeducation), try to lower stress, and work on their relationships with others. There are also medicines that can help them have more stable moods. Even though it can be tough, there's hope and help for people with bipolar disorder.
-
12 Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia is a challenging condition that affects approximately 24 million people worldwide, which is about 1 in every 300 individuals (1). Sadly, those living with schizophrenia tend to have a shorter life expectancy, typically 10 to 20 years less than the general population (4).Schizophrenia is characterized by significant changes in how people perceive the world and behave. People with this condition may experience persistent delusions, which are false beliefs, or hallucinations, where they hear or see things that aren't real. Their thoughts can become disorganized and confusing, leading to highly disorganized behavior or extreme restlessness and agitation.Furthermore, individuals with schizophrenia often struggle with their cognitive functioning, which includes things like memory and problem-solving. However, it's essential to know that there are effective treatments available. Medications can help manage symptoms, and psychoeducation provides valuable information and coping strategies. Involving families in the treatment process through interventions can be incredibly supportive. Additionally, psychosocial rehabilitation programs offer vital assistance in daily life. Despite the challenges, there is hope and help for individuals living with schizophrenia.
-
Advertisement
13 Mental health

The burden has decreased since 1990. The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, along with the enduring effects of war and violence, has placed a heightened emphasis on the importance of addressing mental health concerns. It's crucial to understand how these recent events have influenced the prevalence and impact of mental disorders, especially in the years following 2022. In light of these evolving challenges, countries are tasked with adapting and enhancing their mental health responses to effectively meet the needs of their populations and alleviate the growing burden on mental health systems.